Agile has reshaped the way projects are managed in today’s fast-evolving industries. Designed for flexibility and responsiveness, Agile allows teams to break projects into smaller, iterative cycles delivering value continuously rather than all at once. This approach has become especially valuable in environments where requirements are likely to change and fast feedback is essential for success.
Why Agile Fits Today’s Work Culture
In modern business settings, agility is more than just a buzzword, it’s a necessity. Traditional project management methods often fall short when conditions shift unexpectedly. Agile solves this problem by enabling teams to work in short sprints, make real-time adjustments, and incorporate feedback early and often. This keeps work aligned with stakeholder needs and reduces the risks associated with long, rigid plans. Enhance your project management skills and stay ahead in today’s fast-paced industry with our comprehensive Agile Certification Course.

Core Beliefs That Shape Agile
Agile is guided by a clear set of values and principles that promote teamwork, flexibility, and customer satisfaction. These ideas are laid out in the Agile Manifesto and remain at the heart of every Agile framework.
Agile encourages:
Individuals and interactions over strict adherence to tools
Working outputs over excessive documentation
Ongoing collaboration with stakeholders
Embracing change rather than resisting it
These core beliefs guide teams to remain adaptable, communicative, and focused on delivering functional results.
Agile vs Traditional Project Management
Unlike conventional approaches, which follow a fixed path from start to finish, Agile is built around short development cycles known as sprints. This method allows for regular reviews and changes, ensuring the product evolves alongside user expectations. Rather than waiting until the end of a project to deliver results, Agile focuses on steady progress, constant evaluation, and continuous improvement.
Understanding the Agile Cycle
Each Agile project progresses through repeating phases that include planning, execution, testing, review, and adaptation. At the beginning of each sprint, teams set clear goals. As work progresses, feedback is collected and used to guide the next steps. This cycle creates a rhythm that keeps everyone aligned while allowing space to correct course whenever necessary.
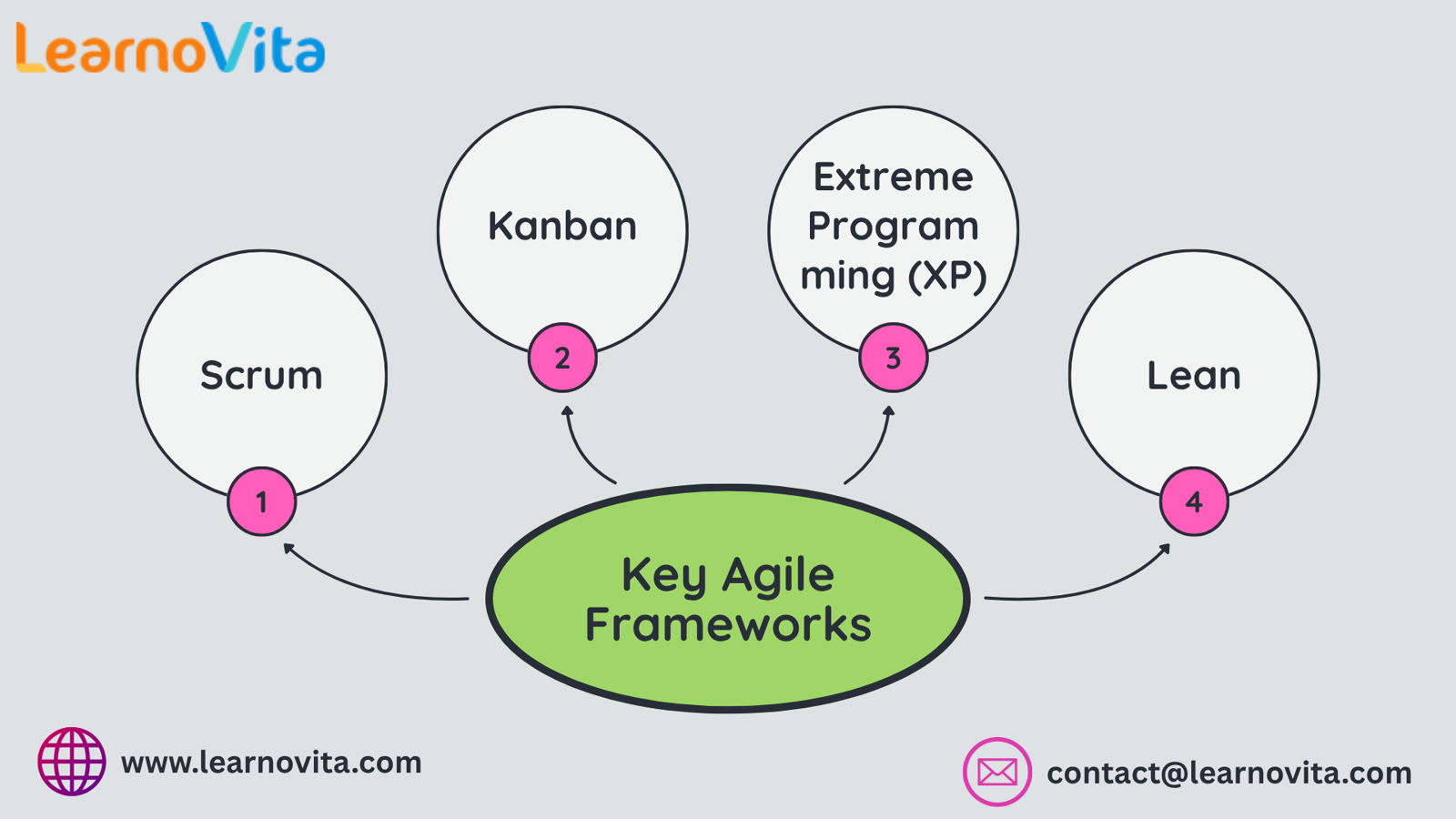
Types of Agile Frameworks
Agile can be implemented through different frameworks, each offering its own structure and tools.
Popular Agile frameworks include:
Scrum – Based on short sprints, predefined roles, and team ceremonies
Kanban – Visualizes workflow with task boards and work-in-progress limits
Extreme Programming (XP) – Combines Agile with rigorous development practices
Lean – Focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value
Each framework can be customized to suit the team’s size, goals, and workflow. Kickstart your career with the Best Training & Placement Program designed to equip you with in-demand skills and guaranteed job support.
Team Dynamics in Agile Projects
Agile teams function best when responsibilities are clear, but flexibility is encouraged. Unlike rigid hierarchies, Agile promotes shared ownership of results.
Agile team roles typically include:
Product Owner – Defines priorities and ensures work reflects user needs
Scrum Master – Facilitates the Agile process and helps resolve team obstacles
Development Team – A cross-functional group that executes the work
This structure supports open collaboration and faster decision-making within a project.
Agile Activities and Tools That Drive Success
Agile relies on frequent check-ins and visible workflows to keep progress transparent and communication consistent.
Key Agile practices include:
Sprint Planning – Outlining goals and tasks at the start of each sprint
Daily Stand-ups – Quick team meetings to report progress and flag blockers
Sprint Reviews – Showcasing completed work and gathering feedback
Retrospectives – Reflecting on what worked well and what needs to improve
Project management tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana help teams visualize tasks and maintain flow.
Common Hurdles in Agile Adoption
Transitioning to Agile can pose initial challenges. Team members may resist changing long-established habits, and leadership may struggle to adjust from control-driven methods to trust-based collaboration. Additionally, without proper training and clarity in roles, implementation may falter. To succeed, organizations must embrace a culture of experimentation, continuous learning, and open communication.
Benefits of Agile in Action
Teams that use Agile effectively often experience shorter delivery timelines, higher product quality, and more satisfied clients. Agile ensures feedback is incorporated throughout the project, not just at the end. This results in products that are more aligned with user needs. Additionally, Agile fosters a healthier team culture and people feel more engaged, responsible, and aligned with the project’s outcomes.
Getting Started with Agile the Right Way
Starting small is often the best way to adopt Agile. Select a low-risk project, choose a basic framework like Scrum or Kanban, and introduce the team to key ceremonies. Use lightweight tools to track tasks and encourage regular team discussions. Most importantly, focus on building an Agile mindset: one that values collaboration, feedback, and adaptability over rigid control and detailed planning.
Final Thoughts
Agile has become the go-to approach for modern project management because it supports speed, flexibility, and continuous improvement. It transforms the way teams plan, build, and deliver work people and value at the center. For anyone stepping into the world of project management, learning the basics of Agile provides the foundation for navigating uncertainty and delivering lasting impact.


Write a comment ...